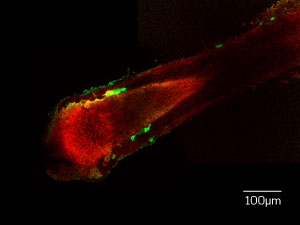
Isolated, growing human hair follicle, showing mitochondrial membrane potential (red) and reactive oxygen species (green).
© 2018 A*STAR Institute of Medical Biology
Understanding the energy it takes to grow a strand of hair could hold the key to ensuring women end their lives with a wonderful bouffant.
Recent research by A*STAR scientist Thomas Dawson and his team, in collaboration with researchers from the Medical University of South Carolina Pharmacy School Department of Drug Discovery, suggests that the slowing of the metabolism as we age could be a driver of ‘chronogenetic alopecia’ or age-related hair loss, a condition that predominantly affects women.
Dawson, from A*STAR’s Institute of Medical Biology, says that the majority of hair research to date has focused on balding men — even medical books from Cleopatra’s reign contained formulas to cure hair loss.
His latest study uses cutting-edge laser microscopy on plucked human and bovine hair to better understand hair growth at a molecular and metabolic level.
In particular Dawson’s team is examining the role that mitochondrial metabolism and its by-product, reactive oxygen, play in the bioenergetics of the hair follicle.
“As we age mitochondrial energy production slows, so we end up with a reduced ability to make good hair,” he says. “Any time there is a screw up in your metabolism you lose hair. People who go on crash diets, students undertaking exams, all will lose hair — only a small change in metabolism makes a noticeable difference.”
Hair growth is an energy-intensive process, Dawson says, with an average human growing almost two meters of hair over their body per hour.
“It takes about 670 kilojoules of energy to grow one gram of hair, which is the equivalent of six minutes of intense exercise using both arms and legs,” Dawson points out.
He believes the cells that create the hair multiply and synthesize biomass so quickly that they burn enormous amounts of energy much like “driving a car with both feet down hard on the gas”.
“The motor is running absolutely flat out and as a result there is excess reactive oxygen generation in the hair follicle that actually damages the structure. The follicle then loses its ability to continue to operate at full form over time.”
The team also uncovered a previously unknown region in the hair shaft which they called the ‘ring of fire’ because it is a major source of reactive oxygen species.

Thomas Dawson (center) and his research group at the Institute of Medical Biology
© 2018 A*STAR Institute of Medical Biology
Dawson says this study shows that hair follicles and growth are more complex than previously thought, and that quelling the formation of reactive oxygen species and maintaining mitochondrial metabolism could be key to improving hair quality as we age.
“If we use materials such as leave-on creams or lotions that alter metabolism you can change the way hair grows and make follicles survive longer and produce better hair.”
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Institute of Medical Biology. For more information about the team’s research, please visit the Hair and Skin Health webpage.



